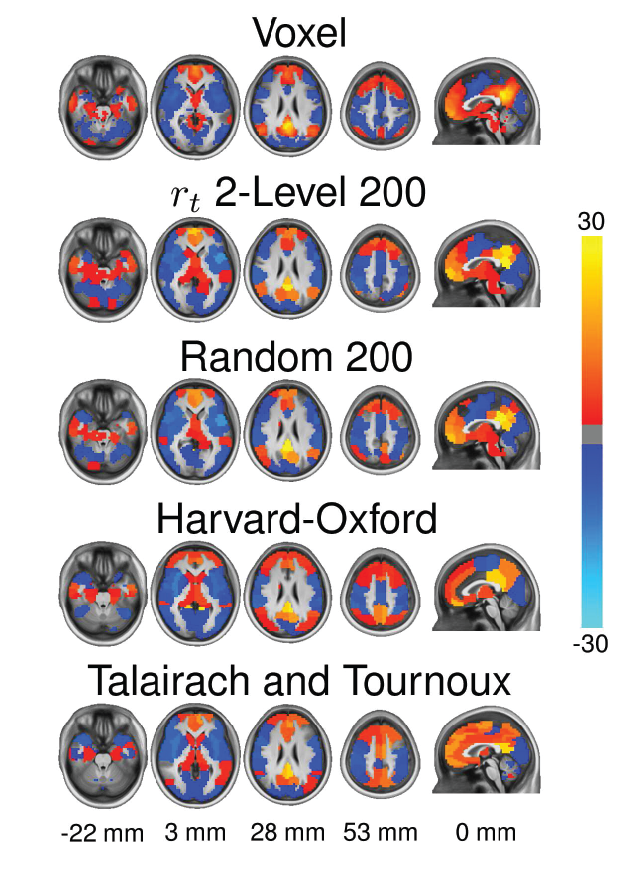
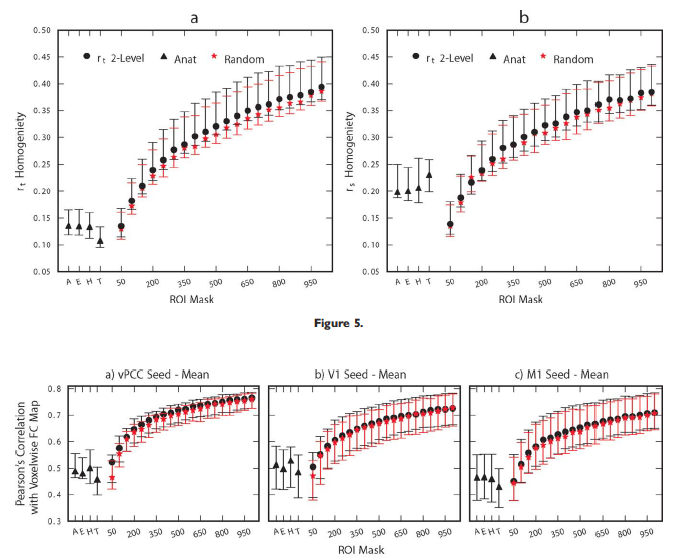
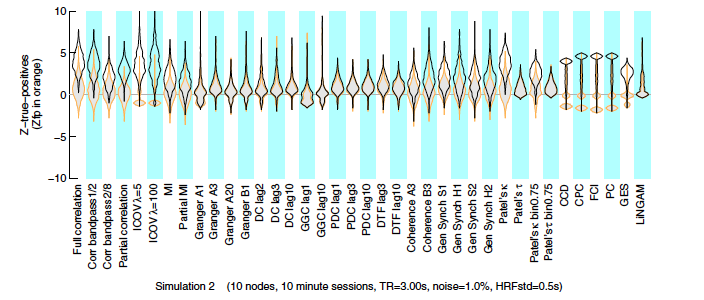
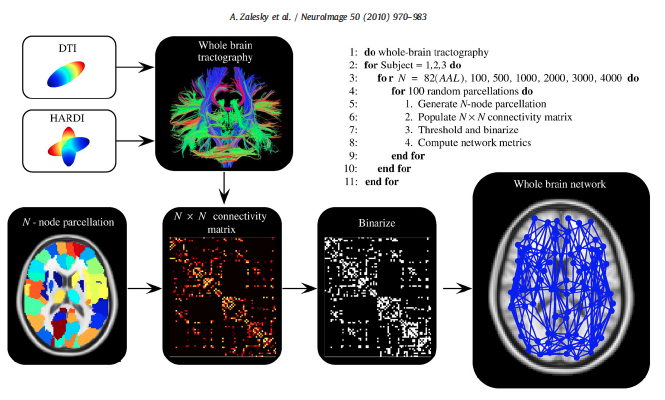
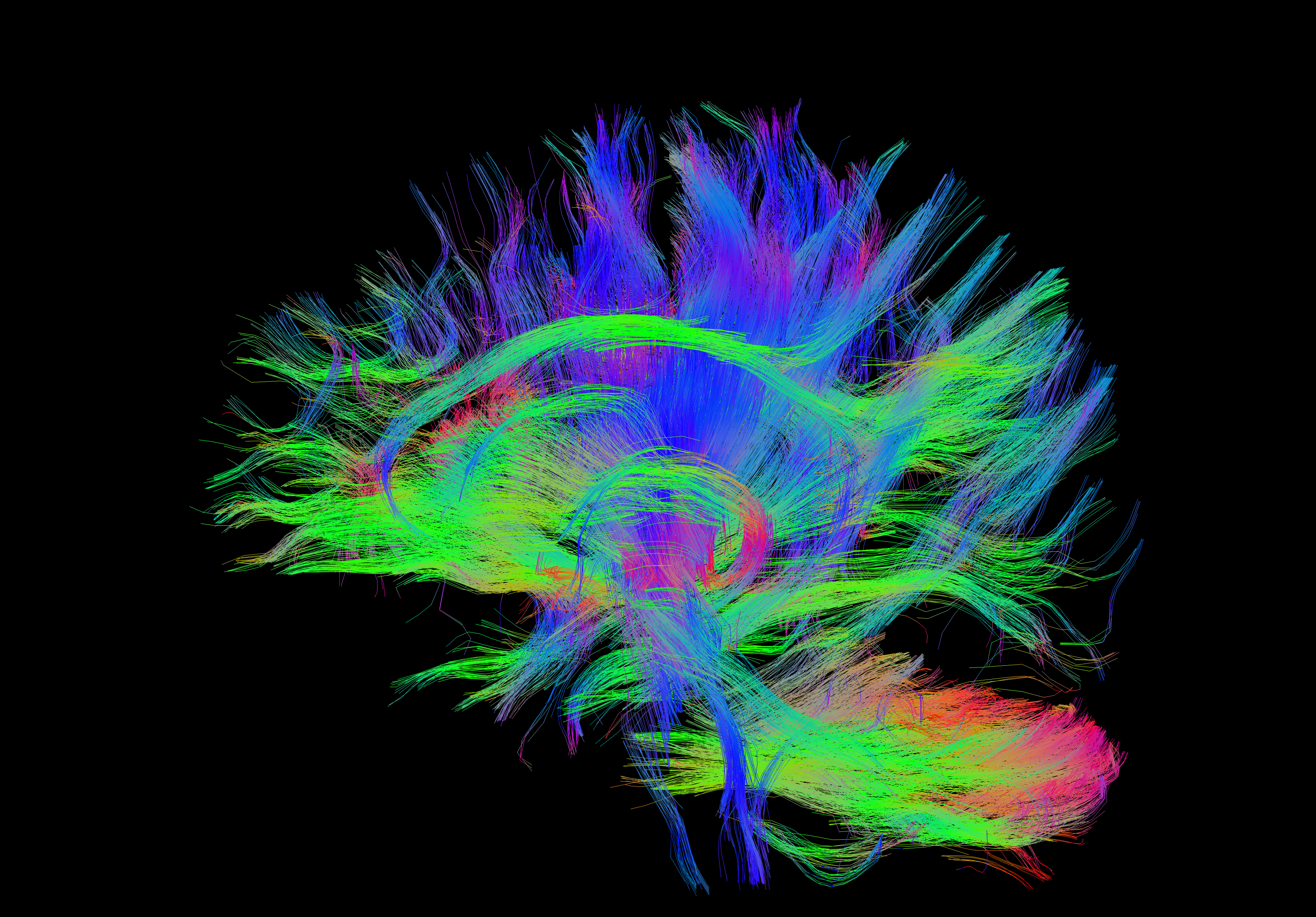
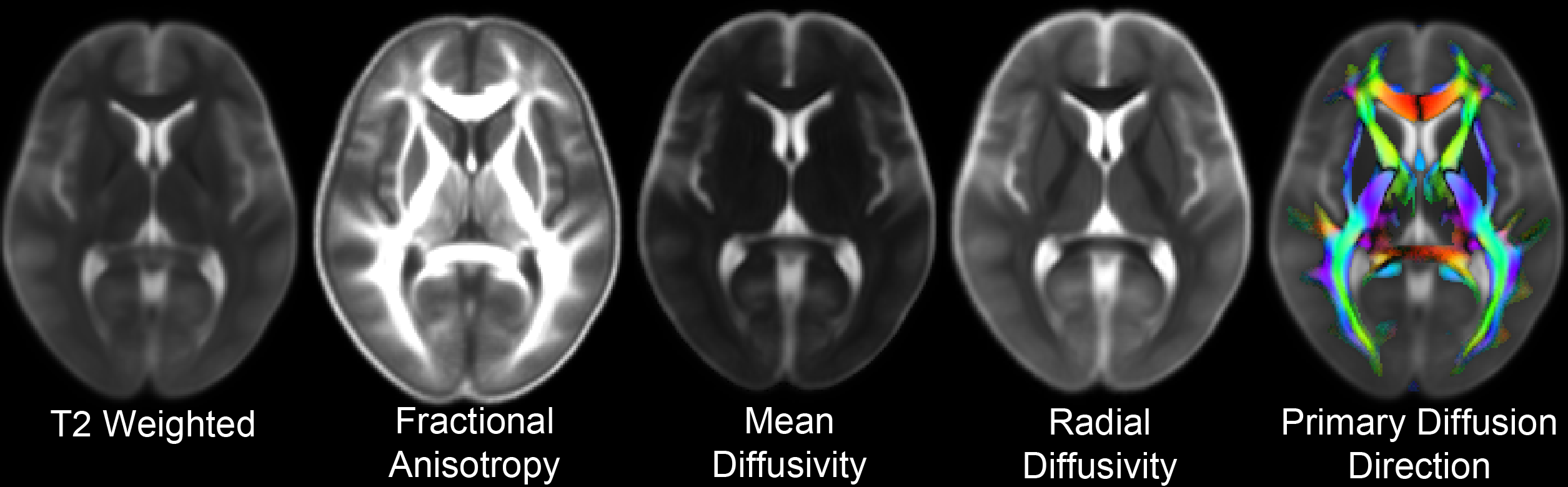
Brain Areas
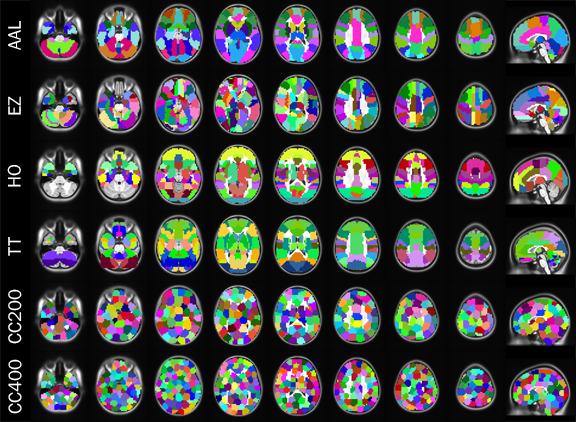
- To construct a connectome graph, you must first choose the areas to use as graph nodes
- Voxels are a logical choice, but will result in very large connectomes
- Alternatives are to use brain atlases derived from cytoarchitectonics, cortical landmarks, or from clustering data